Contents
日出日没計算、やってみよう

この文書の目的
がらくた作りである。私は専門家でもなんでもないので、ここに書くことの正確性については知ったことではないし、興味もない。自分の実用に十分であればそれでよい。
また、WordPress と MathJax 連携についての雰囲気を知って欲しい、というのも密かな目標である。こういうのがアカデミックな世界でしか知られないのは勿体無いし、学者が知らないのだとしたらもっと勿体無い。大学教養レベル程度を記憶している理系の人間であれば、数学にそれほど長けていなくても「美しい数式」が理解を早めることもあるのは、実感としてある。(なにせ私がそうだから。正直数学はちっとも得意じゃない。)なお「美しい数式と美しいドキュメント作り」なら、Sphinxを知って欲しい。こちらも latex または MathJax と連携出来る。
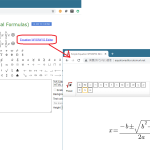
数式部分で右クリックして…
倍率設定をお好みに合わせて変更すると、読みやすさが違うので、試してみて欲しい。本文フォントサイズの 80% か 120%、つまり、数式部分がハッキリと識別できるだけでかなり印象が変わる。
一応理論的な話
門外漢でも WikiPedia さえあれば!
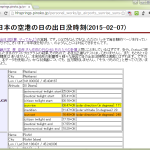
NOAA (アメリカ海洋大気庁)でサービスされている演算のうち「旧」版と、英語版 WIKIPEDIA のSunrise_equation で説明されている内容がどうやら一致しているようである。(WIKIPEDIA の External links, References から推察。)
検証可能な演算(式)が掲載されている(容易に入手可能な)資料は数少ないため、ここではSunrise_equation をひとまず検討するが、実際には他にもいくつも選択肢があり、どれを利用してもあまり大差はなさそうであった。(例えば http://www.hoshi-lab.info/env/solar-j.html は javascript で書かれているため、他の言語への移植は比較的容易である。)
わかったフリして書くけれど – これから書くことはほぼ Wikipedia の写経である
まず演算対象日付のユリウス通日(Julian Day)が必要である。
グレコリオ歴からは、 \(\lfloor x \rfloor\) を床関数、対象グレゴリオ暦(UTC)が year.month.day hour:minute:second であるとし、以下の手順で求めることが出来る:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
JDN &=& day \;+\;
\lfloor \displaystyle \frac{153 m \;+\; 2}{5} \rfloor \;+\; 365 y \;+\;
\lfloor \displaystyle \frac{y}{4} \rfloor \;-
\lfloor \displaystyle \frac{y}{100} \rfloor \;+
\lfloor \displaystyle \frac{y}{400} \rfloor \;-\; 32045 \\
& & \\
JD &=& JDN \;+\; \displaystyle \frac{hour \;-\; 12}{24} + \displaystyle \frac{minute}{24 \times 60} + \displaystyle \frac{second}{24 \times 60 \times 60}
\end{array}
\)
ただし:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
a &=& \lfloor \displaystyle \frac{14 \;-\; month}{12} \rfloor \\
& & \\
y &=& year \;-\; 4800 \;-\; a \\
& & \\
m &=& month \;+\; 12 a \;-\; 3
\end{array}
\)
当然のことながら、日本時間から算出する場合は、 JD = の式に直接タイムゾーンを加味しても良いし、予め UTC にしてから演算しても良い。(なお、この演算を 2000/1/1 12:00:00 UTC に対して行うと JD = 2451545.0 となる。)
次に 2000/1/1 から数えた Julian Cycle (ユリウス周期、つまり、公転した周回数)を求める:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
n &=& \mathrm{round}(JD \;-\; 2451545.0009 \;-\; l_w / 360^\circ)
\end{array}
\)
ここで、 \(l_w\) は観測地点の(地球の)経度であるが、西経が正、東経が負である。
続いて、「the Julian date of solar noon (太陽時における正午のユリウス通日)」について、実際の演算を行う前に用いる中間結果としての近似値を求めておく:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
J^{*} &=& 2451545.0009 \;+\; l_w / 360^\circ \;+\; n
\end{array}
\)
この結果を用いて「Solar Mean Anomaly (太陽の平均近点角)」を求める:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
M &=& (357.5291 \;+\; 0.98560028 (J^{*} \;-\; 2451545)) \bmod{360}
\end{array}
\)
そしてこの \(M\) から、「Equation of Center (中心差)」(the true anomaly – the mean anomaly)が求まる:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
C &=& 1.9148 \sin(M) \;+\; 0.0200 \sin(2M) \;+\; 0.0003 \sin(3M)
\end{array}
\)
これにより「Ecliptic Longitude (黄道座標経度)」が以下で求まる:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
\lambda &=& (M \;+\; 102.9372 \;+\; C \;+\; 180) \bmod{360}
\end{array}
\)
(経度と名前がついているが地球上の経度と同じものではない。)
ここまでの演算で「Solar Transit (または Solar Noon) (太陽時における正午)」が求まる:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
J_{transit} &=& J^{*} \;+\; 0.0053 \sin(M) \;-\; 0.0069 \sin(2 \lambda)
\end{array}
\)
そして「Declination of the Sun (太陽の傾き)」が求まる:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin\delta = \sin\lambda \; \sin23.45^\circ
\end{array}
\)
(\(23.45^\circ\) は地球の地軸の傾きに相当する値、であろう、たぶん。)
そして、「Hour Angle (角速度相当の値)」を求める( \(h\) は観測地点の標高(m)、 \(\Phi\) は地球の緯度(北緯が正)):
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
\cos \omega_0 = \displaystyle\frac{\sin(-0.83 \;-\; 2.076^\circ \sqrt{h} / 60^\circ) \;-\; \sin\Phi \sin\delta}{\cos\Phi \cos\delta}
\end{array}
\)
明解な説明があまりないため判然としないものの、どうやら 0.83 項部分は沈み込み(apparent dip)、屈折(terrestrial refraction)の両方を考慮している項らしい。
そしてようやく目的のもの:
\(
\begin{array}{rcl}
J_{set} &=& 2451545.0009 \;+\; (\omega_0 \;+\; l_w) / 360^\circ \;+\; n \;+\; 0.0053 \sin M \;-\; 0.0069 \sin 2\lambda \\
& & \\
J_{rise} &=& J_{transit} \;-\; (J_{set} \;-\; J_{transit})
\end{array}
\)
これが求めたい日出日没時刻である。この演算結果はユリウス通日であるが、実用上はあまり困らない。なぜなら、最初に必要なユリウス通日の計算結果からの差がほぼ目的のものであるため。(つまりは 00:00 のユリウス通日を手持ちであればそれを引けば 00:00 からの積算秒が得られるため。)
この計算を忠実に愚直に実装してみたところ、NOAA の「新版」 http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/grad/solcalc/ での
計算結果とは 1分程度は違ってくるようである。おそらく計算の改善が行われた結果なのであろう。
こんなサイトもありますよ
http://www.hoshi-lab.info/env/solar-j.html
これは書籍のサポートサイトのようだ。「薄明(twilight)」も計算してくれる。
Python で – 作ってみた、のだと思う
実はこれをやったのは随分前なので、どこかから持ってきたのか移植したのか上述の計算方法で自力で作ったのかが全く記憶にない。スタイルは自分の「最も雑にやったときのもの」そのものなので、作ったんだと思う。
1 import math
2
3 # calculate Julius year (year from 2000/1/1, for variable "t")
4 def jy(yy, mm, dd, h, m, s, i): # yy/mm/dd h:m:s, i: time difference
5 #yy -= 2000
6 #if (mm <= 2):
7 # mm += 12
8 # yy -= 1
9 #
10 #k = 365 * yy + 30 * mm + dd - 33.5 - i / 24.0 + math.floor(3 * (mm + 1) / 5.0)
11 # + math.floor(yy / 4.0) - math.floor(yy / 100.0) + math.floor(yy / 400.0)
12 #k += ((s / 60.0 + m) / 60 + h) / 24.0 # plus time
13 #k += (65 + yy) / 86400.0 # plus delta T
14 #return k / 365.25
15 a_ = (14 - mm) / 12
16 y_ = yy + 4800 - a_
17 m_ = mm + 12 * a_ - 3
18 JDN_ = dd + (153 * m_ + 2) / 5 + 365 * y_ + y_ / 4 - y_ / 100 + y_ / 400 - 32045
19 JD_ = JDN_ + (h - 12 - i) / 24. + m / 1440. + s / 86400.
20 return JD_
21
22 jy_ = jy(2013, 4, 2, 0, 0, 0, 9)
23 lw_ = -139.7909446414986
24 le_ = -lw_
25 phi_ = 35.54131474808071
26 height_ = 0.
27
28 naster_ = jy_ - 2451545.0009 - lw_ / 360.
29 #naster_ = jy_ - 2451545.0009 + le_ / 360.
30 n_ = round(naster_) #
31 jaster_ = 2451545.0009 + lw_ / 360. + n_
32 #jaster_ = 2451545.0009 - le_ / 360. + n_
33 M_ = (357.5291 + 0.98560028 * (jaster_ - 2451545)) % 360 #
34 C_ = 1.9148 * math.sin(math.radians(M_)) + 0.0200 * math.sin(math.radians(2 * M_)) + 0.0003 * math.sin(math.radians(3 * M_))
35 lambda_ = (M_ + 102.9372 + C_ + 180.) % 360
36 jtransit_ = jaster_ + 0.0053 * math.sin(math.radians(M_)) - 0.0069 * math.sin(math.radians(2 * lambda_))
37 sin_delta_ = math.sin(math.radians(lambda_)) * math.sin(math.radians(23.45))
38 delta_ = math.degrees(math.asin(sin_delta_))
39
40 w0_ = math.degrees(
41 math.acos((math.sin(math.radians(-0.83 - 2.076 * math.sqrt(height_) / 60.)) - math.sin(math.radians(phi_)) * sin_delta_) /
42 (math.cos(math.radians(phi_)) * math.cos(math.radians(delta_))))
43 )
44
45 #jset_ = 2451545.0009 + (w0_ + lw_) / 360. + n_ + 0.0053 * math.sin(math.radians(M_)) - 0.0069 * math.sin(math.radians(2 * lambda_))
46 jset_ = 2451545.0009 + (w0_ - le_) / 360. + n_ + 0.0053 * math.sin(math.radians(M_)) - 0.0069 * math.sin(math.radians(2 * lambda_))
47 jrise_ = jtransit_ - (jset_ - jtransit_)
48 #print(jrise_, jset_)
49
50 jrise_h_ = int((jrise_ - jy_) * 24)
51 print(jrise_h_, ((jrise_ - jy_) * 1440) % 60)
52 jtransit_h_ = int((jtransit_ - jy_) * 24)
53 print(jtransit_h_, ((jtransit_ - jy_) * 1440) % 60)
54 jset_h_ = int((jset_ - jy_) * 24)
55 print(jset_h_, ((jset_ - jy_) * 1440) % 60)
56
57 #print(__timefromdecimalday(jrise_*(1e11)), __timefromdecimalday(jset_*(1e11)))
プロトタイプ丸出しで、多分緯度経度は羽田空港あたりを直値で指定している。日付も「jy(2013, 4, 2, 0, 0, 0, 9)」つまり2013年の4月2日。そうか。作ったのはこの日か。
Python で – https://github.com/hozn/bafs/blob/master/weather/sunrise.pyをコピーしてきて書き換え
スタイルは自分のものではないし、「ネイティブな」英語コメントが入っているところをみると、どこかから持ってきたのだろうか? 書き換えようとしていた形跡もある。と改めて検索してわかった。https://github.com/hozn/bafs/blob/master/weather/sunrise.pyが元。pytz 依存だったので class LocalTimezone 部分をインラインに展開したみたい。
1 # original: https://github.com/hozn/bafs/blob/master/weather/sunrise.py
2 from math import cos,sin,acos,asin,tan
3 from math import degrees as deg, radians as rad
4 from datetime import date,datetime,time,tzinfo,timedelta
5
6 # this module is not provided here. See text.
7 #from timezone import LocalTimezone
8 # ------------------------------------------------
9 import time as _time
10 class LocalTimezone(tzinfo):
11 def __init__(self):
12 self.STDOFFSET = timedelta(seconds=-_time.timezone)
13 if _time.daylight:
14 self.DSTOFFSET = timedelta(seconds=-_time.altzone)
15 else:
16 self.DSTOFFSET = self.STDOFFSET
17
18 self.DSTDIFF = self.DSTOFFSET - self.STDOFFSET
19
20 def utcoffset(self, dt):
21 if self._isdst(dt):
22 return self.DSTOFFSET
23 else:
24 return self.STDOFFSET
25
26 def dst(self, dt):
27 if self._isdst(dt):
28 return self.DSTDIFF
29 else:
30 return timedelta(0)
31
32 def tzname(self, dt):
33 return _time.tzname[self._isdst(dt)]
34
35 def _isdst(self, dt):
36 tt = (dt.year, dt.month, dt.day, dt.hour, dt.minute, dt.second,
37 dt.weekday(), 0, 0)
38 stamp = _time.mktime(tt)
39 tt = _time.localtime(stamp)
40 return tt.tm_isdst > 0
41 # ------------------------------------------------
42
43 class sun(object):
44 """
45 Calculate sunrise and sunset based on equations from NOAA
46
47 http://www.srrb.noaa.gov/highlights/sunrise/calcdetails.html
48
49 typical use, calculating the sunrise at the present day:
50
51 import datetime
52 import sunrise
53 s = sun(lat=49,lon=3)
54 print('sunrise at ',s.sunrise(when=datetime.datetime.now())
55 """
56 def __init__(self,lat=52.37,lon=4.90): # default Amsterdam
57 self.lat = lat
58 self.lon = lon
59
60 def sunrise(self,when=None):
61 """
62 return the time of sunrise as a datetime.time object
63 when is a datetime.datetime object. If none is given
64 a local time zone is assumed (including daylight saving
65 if present)
66 """
67 if when is None : when = datetime.now(tz=LocalTimezone())
68 self.__preptime(when)
69 self.__calc()
70 return sun.__timefromdecimalday(self.sunrise_t)
71
72 def sunset(self,when=None):
73 if when is None : when = datetime.now(tz=LocalTimezone())
74 self.__preptime(when)
75 self.__calc()
76 return sun.__timefromdecimalday(self.sunset_t)
77
78 def solarnoon(self,when=None):
79 if when is None : when = datetime.now(tz=LocalTimezone())
80 self.__preptime(when)
81 self.__calc()
82 return sun.__timefromdecimalday(self.solarnoon_t)
83
84 @staticmethod
85 def __timefromdecimalday(day):
86 """
87 returns a datetime.time object.
88
89 day is a decimal day between 0.0 and 1.0, e.g. noon = 0.5
90 """
91 hours = 24.0*day
92 h = int(hours)%24
93 minutes= ((hours-h)*60)%60
94 m = int(minutes)
95 seconds= (minutes-m)*60
96 s = int(seconds)
97 return time(hour=h,minute=m,second=s)
98
99 def __preptime(self,when):
100 """
101 Extract information in a suitable format from when,
102 a datetime.datetime object.
103 """
104 # datetime days are numbered in the Gregorian calendar
105 # while the calculations from NOAA are distibuted as
106 # OpenOffice spreadsheets with days numbered from
107 # 1/1/1900. The difference are those numbers taken for
108 # 18/12/2010
109 self.day = when.toordinal()-(734124-40529)
110 t=when.time()
111 self.time= (t.hour + t.minute/60.0 + t.second/3600.0)/24.0
112
113 self.timezone=0
114 offset=when.utcoffset()
115 if not offset is None:
116 #self.timezone=offset.seconds/3600.0
117 self.timezone=offset.seconds/3600.0 + (offset.days * 24)
118
119 def __calc(self):
120 """
121 Perform the actual calculations for sunrise, sunset and
122 a number of related quantities.
123
124 The results are stored in the instance variables
125 sunrise_t, sunset_t and solarnoon_t
126 """
127 timezone = self.timezone # in hours, east is positive
128 longitude = self.lon # in decimal degrees, east is positive
129 latitude = self.lat # in decimal degrees, north is positive
130
131 time = self.time # percentage past midnight, i.e. noon is 0.5
132 day = self.day # daynumber 1 = 1/1/1900
133
134 Jday = day+2415018.5+time-timezone/24 # Julian day
135 Jcent = (Jday-2451545)/36525 # Julian century
136
137 Manom = 357.52911+Jcent*(35999.05029-0.0001537*Jcent)
138 Mlong = 280.46646+Jcent*(36000.76983+Jcent*0.0003032)%360
139 Eccent = 0.016708634-Jcent*(0.000042037+0.0001537*Jcent)
140 Mobliq = 23+(26+((21.448-Jcent*(46.815+Jcent*(0.00059-Jcent*0.001813))))/60)/60
141 obliq = Mobliq+0.00256*cos(rad(125.04-1934.136*Jcent))
142 vary = tan(rad(obliq/2))*tan(rad(obliq/2))
143 Seqcent = sin(rad(Manom))*(1.914602-Jcent*(0.004817+0.000014*Jcent))+sin(rad(2*Manom))*(0.019993-0.000101*Jcent)+sin(rad(3*Manom))*0.000289
144 Struelong = Mlong+Seqcent
145 Sapplong = Struelong-0.00569-0.00478*sin(rad(125.04-1934.136*Jcent))
146 declination = deg(asin(sin(rad(obliq))*sin(rad(Sapplong))))
147
148 eqtime = 4*deg(vary*sin(2*rad(Mlong))-2*Eccent*sin(rad(Manom))+4*Eccent*vary*sin(rad(Manom))*cos(2*rad(Mlong))-0.5*vary*vary*sin(4*rad(Mlong))-1.25*Eccent*Eccent*sin(2*rad(Manom)))
149
150 hourangle = deg(acos(cos(rad(90.833))/(cos(rad(latitude))*cos(rad(declination)))-tan(rad(latitude))*tan(rad(declination))))
151
152 self.solarnoon_t = (720-4*longitude-eqtime+timezone*60)/1440
153 self.sunrise_t = self.solarnoon_t-hourangle*4/1440
154 self.sunset_t = self.solarnoon_t+hourangle*4/1440
155 #print(self.sunrise_t, self.sunset_t)
156
157 def calc_approx_whole_year(lon, lat, start=datetime(2012, 1, 1, tzinfo=LocalTimezone())):
158 s = sun(lon=lon, lat=lat)
159 for i in range(366):
160 when = start + timedelta(i, 0, 0)
161 yield when, s.sunrise(when=when), s.solarnoon(when=when), s.sunset(when=when)
162
163 if __name__ == "__main__":
164 import sys
165
166 FMT1 = '%m-%d'
167 FMT2 = '%H:%M:%S'
168 for when, sunrise, solarnoon, sunset in calc_approx_whole_year(lon=float(sys.argv[1]), lat=float(sys.argv[2])):
169 print("%s, %s, %s, %s" % (
170 when.strftime(FMT1),
171 sunrise.strftime(FMT2),
172 solarnoon.strftime(FMT2),
173 sunset.strftime(FMT2)))
Python に – 移植したのである
http://www.hoshi-lab.info/env/solar-j.html の javascript を Python に移植したもの。これは憶えてる。計算は多分 NOAA のとは全然違う。やるべきことはそう違うわけはない(結局地軸の傾き・地球の自転・地球の公転・太陽の公転 etc. の関係を計算する)ので、導出が違うのかしらね?
1 import numpy as np
2
3 # sin function using degree
4 def sind(d):
5 return np.sin(np.radians(d))
6
7 # cos function using degree
8 def cosd(d):
9 return np.cos(np.radians(d))
10
11 # tan function using degree
12 def tand(d):
13 return np.tan(np.radians(d))
14
15 # calculate Julius year (year from 2000/1/1, for variable "t")
16 def jy(yy, mm, dd, h, m, s, i): # yy/mm/dd h:m:s, i: time difference
17 yy -= 2000
18 if (mm <= 2):
19 mm += 12
20 yy -= 1
21
22 k = 365 * yy + 30 * mm + dd - 33.5 - i / 24.0 + np.floor(3 * (mm + 1) / 5.0) \
23 + np.floor(yy / 4.0) - np.floor(yy / 100.0) + np.floor(yy / 400.0)
24 k += ((s / 60.0 + m) / 60 + h) / 24.0 # plus time
25 k += (65 + yy) / 86400.0 # plus delta T
26 return k / 365.25
27
28 # solar position1 (celestial longitude, degree)
29 def spls(t): # t: Julius year
30 L = 280.4603 + 360.00769 * t \
31 + (1.9146 - 0.00005 * t) * sind(357.538 + 359.991 * t) \
32 + 0.0200 * sind(355.05 + 719.981 * t) \
33 + 0.0048 * sind(234.95 + 19.341 * t) \
34 + 0.0020 * sind(247.1 + 329.640 * t) \
35 + 0.0018 * sind(297.8 + 4452.67 * t) \
36 + 0.0018 * sind(251.3 + 0.20 * t) \
37 + 0.0015 * sind(343.2 + 450.37 * t) \
38 + 0.0013 * sind( 81.4 + 225.18 * t) \
39 + 0.0008 * sind(132.5 + 659.29 * t) \
40 + 0.0007 * sind(153.3 + 90.38 * t) \
41 + 0.0007 * sind(206.8 + 30.35 * t) \
42 + 0.0006 * sind( 29.8 + 337.18 * t) \
43 + 0.0005 * sind(207.4 + 1.50 * t) \
44 + 0.0005 * sind(291.2 + 22.81 * t) \
45 + 0.0004 * sind(234.9 + 315.56 * t) \
46 + 0.0004 * sind(157.3 + 299.30 * t) \
47 + 0.0004 * sind( 21.1 + 720.02 * t) \
48 + 0.0003 * sind(352.5 + 1079.97 * t) \
49 + 0.0003 * sind(329.7 + 44.43 * t)
50 while (L >= 360):
51 L -= 360
52 while (L < 0):
53 L += 360
54 return L
55
56 # solar position2 (distance, AU)
57 def spds(t): # t: Julius year
58 r = (0.007256 - 0.0000002 * t) * sind(267.54 + 359.991 * t) \
59 + 0.000091 * sind(265.1 + 719.98 * t) \
60 + 0.000030 * sind( 90.0) \
61 + 0.000013 * sind( 27.8 + 4452.67 * t) \
62 + 0.000007 * sind(254 + 450.4 * t) \
63 + 0.000007 * sind(156 + 329.6 * t)
64 r = np.power(10, r)
65 return r
66
67 # solar position3 (declination, degree)
68 def spal(t): # t: Julius year
69 ls = spls(t) ;
70 ep = 23.439291 - 0.000130042 * t
71 al = np.degrees(np.arctan(tand(ls) * cosd(ep)))
72 if ((ls >= 0) and (ls < 180)):
73 while (al < 0):
74 al += 180
75 while (al >= 180):
76 al -= 180
77 else:
78 while (al < 180):
79 al += 180
80 while (al >= 360):
81 al -= 180
82 return al ;
83
84 # solar position4 (the right ascension, degree)
85 def spdl(t): # t: Julius year
86 ls = spls(t)
87 ep = 23.439291 - 0.000130042 * t
88 dl = np.degrees(np.arcsin(sind(ls) * sind(ep)))
89 return dl
90
91 # Calculate sidereal hour (degree)
92 def sh(t, h, m, s, l, i):
93 # t: julius year, h: hour, m: minute, s: second,
94 # l: longitude, i: time difference
95 d = ((s / 60.0 + m) / 60.0 + h) / 24.0 # elapsed hour (from 0:00 a.m.)
96 th = 100.4606 + 360.007700536 * t + 0.00000003879 * t * t - 15 * i
97 th += l + 360 * d
98 while (th >= 360):
99 th -= 360
100 while (th < 0):
101 th += 360
102 return th
103
104 # Calculating the seeming horizon altitude "sa"(degree)
105 def eandp(alt, ds): # subfunction for altitude and parallax
106 e = 0.035333333 * np.sqrt(alt)
107 p = 0.002442818 / ds
108 return p - e
109
110 def sa(alt, ds): # alt: altitude (m), ds: solar distance (AU)
111 s = 0.266994444 / ds
112 r = 0.585555555
113 k = eandp(alt,ds) - s - r
114 return k
115
116 # Calculating solar alititude (degree) {
117 def soal(la, th, al, dl):
118 # la: latitude, th: sidereal hour,
119 # al: solar declination, dl: right ascension
120 h = sind(dl) * sind(la) + cosd(dl) * cosd(la) * cosd(th - al)
121 h = np.degrees(np.arcsin(h))
122 return h
123
124 # Calculating solar direction (degree) {
125 def sodr(la, th, al, dl):
126 # la: latitude, th: sidereal hour,
127 # al: solar declination, dl: right ascension
128 t = th - al
129 dc = -cosd(dl) * sind(t)
130 dm = sind(dl) * sind(la) - cosd(dl) * cosd(la) * cosd(t)
131 if (dm == 0):
132 st = sind(t)
133 if (st > 0):
134 dr = -90
135 if (st == 0):
136 dr = 9999
137 if (st < 0):
138 dr = 90
139 else:
140 dr = np.degrees(np.arctan(dc / dm))
141 if (dm < 0):
142 dr += 180
143
144 if (dr < 0):
145 dr += 360
146 return dr
147
148 def calc(yy, mm, dd, i, lon, lat, alt=0, hh=-1, m=-1):
149 """
150 return list:
151 item 0: astronomical twilight start
152 item 1: voyage twilight start
153 item 2: citizen twilight start
154 item 3: sun rise
155 item 4: meridian
156 item 5: sun set
157 item 6: citizen twilight end
158 item 7: voyage twilight end
159 item 8: astronomical twilight end
160
161 each item has time, and solar direction (in degrees) if item is sun rise or sun set,
162 solar altitude (in degrees) if item is meridian.
163 """
164 result = []
165
166 t = jy(yy, mm, dd - 1, 23, 59, 0, i)
167 th = sh(t, 23, 59, 0, lon, i)
168 ds = spds(t)
169 ls = spls(t)
170 alp = spal(t)
171 dlt = spdl(t)
172 pht = soal(lat, th, alp, dlt)
173 pdr = sodr(lat, th, alp, dlt)
174
175 for hh in range(0, 24):
176 for m in range(0, 60):
177 t = jy(yy, mm, dd, hh, m, 0, i)
178 th = sh(t, hh, m, 0, lon, i)
179 ds = spds(t)
180 ls = spls(t)
181 alp = spal(t)
182 dlt = spdl(t)
183 ht = soal(lat, th, alp, dlt)
184 dr = sodr(lat, th, alp, dlt)
185 tt = eandp(alt, ds)
186 t1 = tt - 18
187 t2 = tt - 12
188 t3 = tt - 6
189 t4 = sa(alt, ds)
190
191 key = "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:00+%02d" % (yy, mm, dd, hh, m, i)
192
193 if ((pht < t1) and (ht > t1)):
194 result.append((key, None))
195 if ((pht < t2) and (ht > t2)):
196 result.append((key, None))
197 if ((pht < t3) and (ht > t3)):
198 result.append((key, None))
199 if ((pht < t4) and (ht > t4)):
200 result.append((key, np.floor(dr)))
201 if ((pdr < 180) and (dr > 180)):
202 result.append((key, np.floor(ht)))
203 if ((pht > t4) and (ht < t4)):
204 result.append((key, np.floor(dr)))
205 if ((pht > t3) and (ht < t3)):
206 result.append((key, None))
207 if ((pht > t2) and (ht < t2)):
208 result.append((key, None))
209 if ((pht > t1) and (ht < t1)):
210 result.append((key, None))
211 pht = ht
212 pdr = dr
213
214 #f.result.value = ans
215 return result
216
217 if __name__ == '__main__':
218 r = calc(2013, 4, 2, 9, 139.7909446414986, 35.54131474808071, 0.)
219 for k, v in r:
220 print("%s: %s" % (k, v))
あ、これも2013年4月2日だ…。これも羽田空港、かな? どこにも NumPy 使う理由がないのだが、その頃手癖になってたんだろう、意味もなく NumPy 依存になっている。これは Pure Python でも十分書けます。あとね、javascript からダイレクトに移植したので、Python では無意味なセミコロンが入ってますな。不当ではないし文法も正しいけど付けないわなぁ、普通。
「薄明」のコメントで「voyage twilight」と言っている部分、和訳だと「航海薄明」と呼ばれる時間帯で、「nautical twilight」とも言います(en.wikipedia.orgなど参照)。

作らんでもいいのでわ
ワシもそう思う。Googleさんに聞いてみれば良いのでは。実際私がこれをやったのも、「イチイチ理科年表から持ってきてられっか、計算出来ねぇかなぁ?」という「要件」から Google さんに聞いたのであって。もちっと真剣に探せば、自作しないでいいんじゃないかしら。(PyEphem とか。)
2021-06-09追記: NightShade
なんでこのネタがこんなに読まれるのかよくわかってなくて、果たして Python 固有の話だけしてて、迷惑じゃないんだろうか、とも思うんだけれど…。
ここ数週間 cartopy ネタを書いてきたんだけれど、この cartopy の機能の一つに「feature.nightshade」があるのね。使用例はギャラリーにもあるけれど、ワタシ自身でやってみた例もみせとく:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 import os
3 import sys
4 import re
5 from datetime import datetime, timedelta
6 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 import cartopy.crs as ccrs
8 from cartopy.feature.nightshade import Nightshade
9
10
11 def main():
12 # windows ユーザ以外の方は fontproperties は自分でどうにかしなはれ。
13 fontprop = {"fname": "c:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc"}
14
15 ct = (139.691717, 35.689568) # 東京都庁
16 exp_km = 2000
17 exp = 1. / (3600 * ((30 + 27) / 2)) * exp_km * 1000 # 約 exp_km km
18 ext = [ct[0] - exp, ct[0] + exp, ct[1] - exp, ct[1] + exp]
19
20 now = datetime.utcnow().replace(minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
21 for dit in range(1, 6):
22 dt = now + timedelta(hours=dit)
23 tit = str(dt + timedelta(hours=9)) + " JST"
24 #
25 fig = plt.figure()
26 fig.set_size_inches(16.53, 11.69)
27 ax1 = fig.add_subplot(projection=ccrs.Geostationary(ct[0]))
28 ax1.set_extent(ext, ccrs.PlateCarree())
29 ax1.add_wms(
30 wms='https://ows.terrestris.de/osm/service',
31 layers=["OSM-WMS",])
32 ax1.add_feature(Nightshade(dt))
33 ax1.set_title(tit, fontproperties=fontprop)
34 ax1.gridlines(draw_labels=True, dms=True, x_inline=False, y_inline=False)
35 ax1.text(
36 ct[0], ct[1],
37 "lon={:.6f}\nlat= {:.6f}".format(*ct),
38 transform=ccrs.Geodetic()._as_mpl_transform(ax1),
39 fontproperties=fontprop,
40 color='black',
41 bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.5, boxstyle='round'),
42 )
43 plt.savefig(
44 os.path.splitext(
45 os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]))[0] + ".{}.png".format(
46 re.sub(r"[:. -]", "", str(dt))),
47 bbox_inches="tight")
48
49
50 if __name__ == '__main__':
51 main()
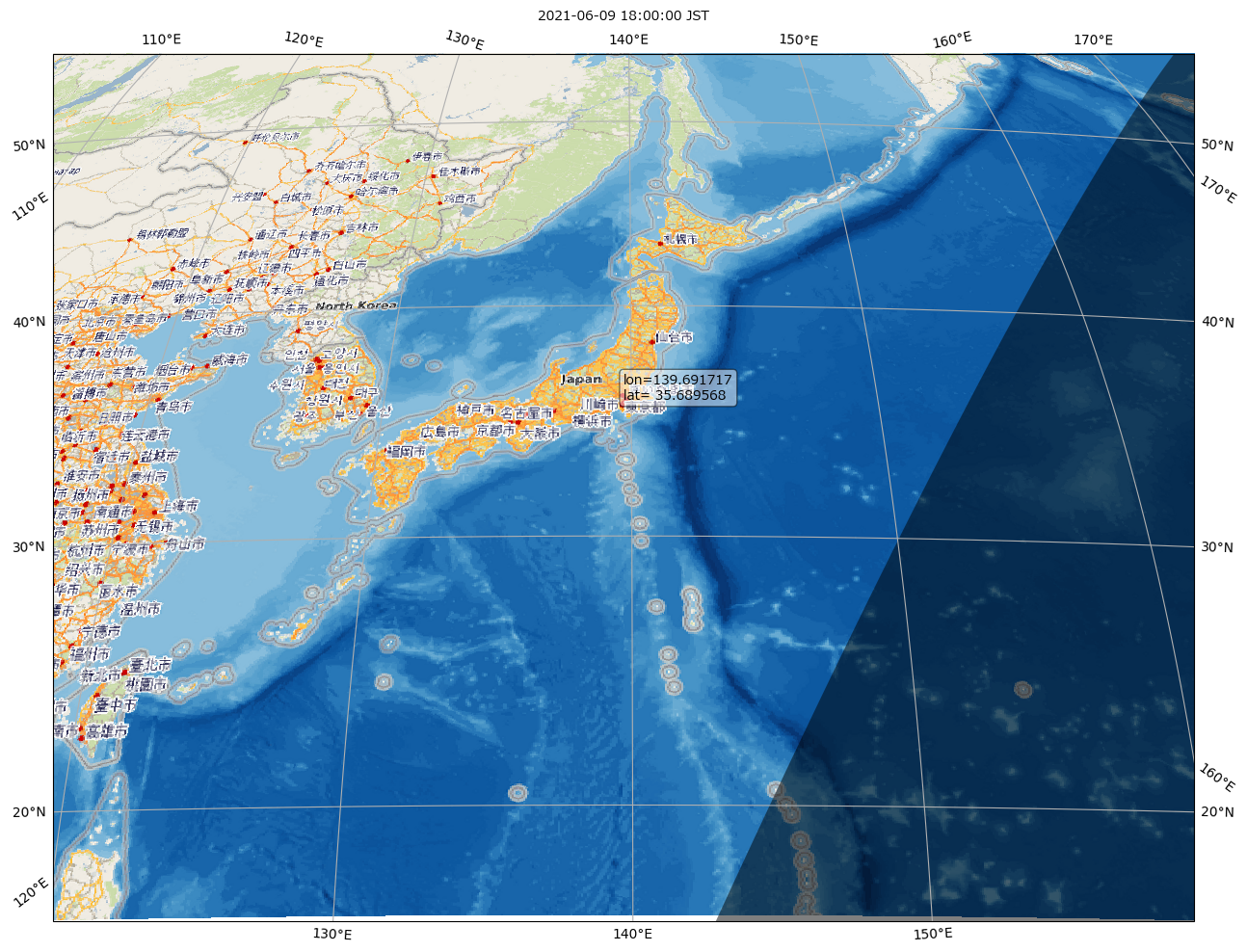
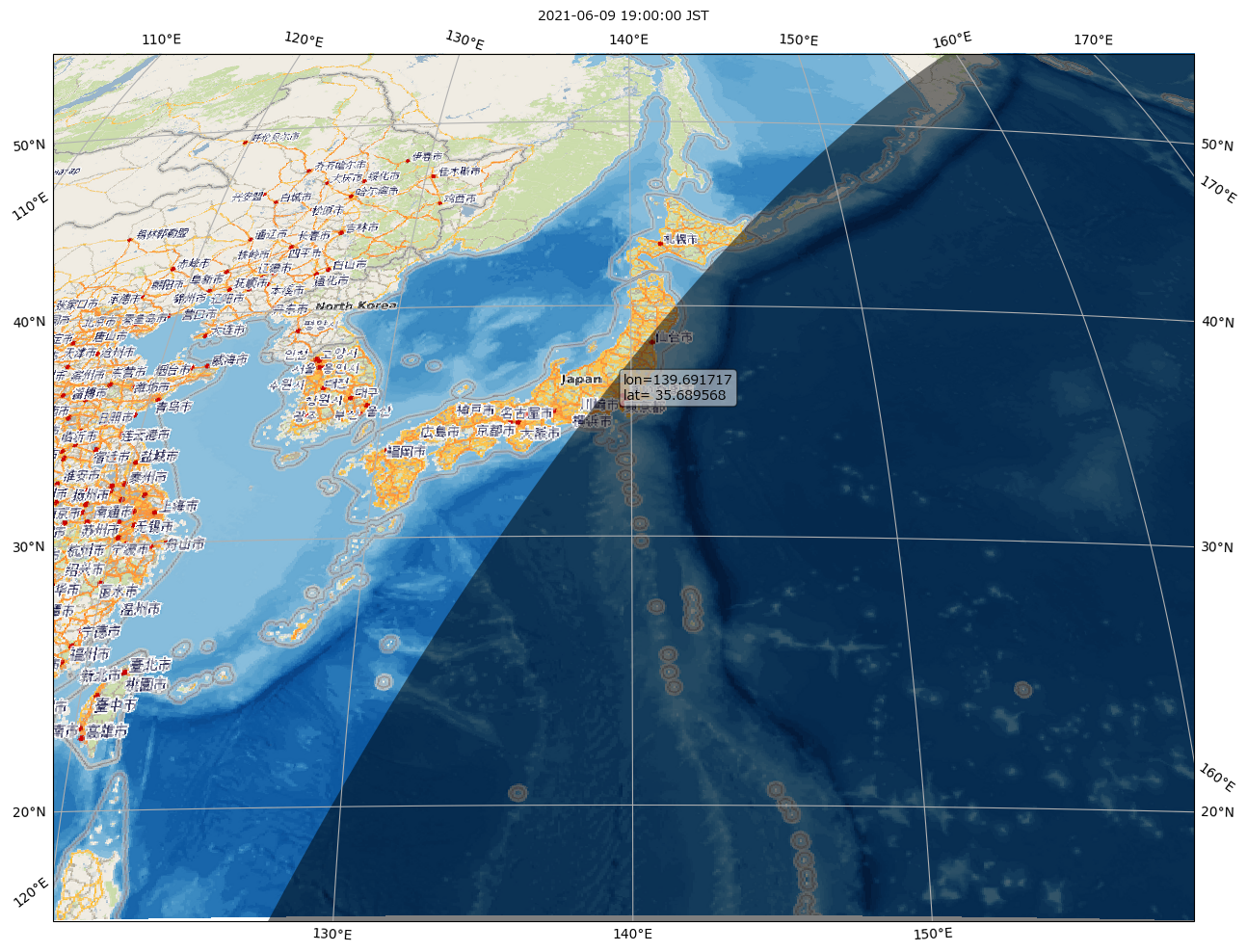
これはまぁ「きゃーすてきぃ」とでも思っておけばいいんだけれど。
「日出日没計算、やってみよう」としての本題。この Nightshade は、無論「地図への描画」が最大のミッションだけど、ワタシがここで書いたのとほとんど同じ実装を pure python で書いている。もちろんそのミッションの中で「日の出日没計算」部分は実装の詳細でありプライベートなので、外から使うようにはなってないけれど、まぁコピペして使うとか考えてもいいんじゃない? (やりたいことによる。時刻を求めるとかをやってるわけではなくて、solar position を求めるとこまでしかやってない。)
コメントによれば、NightShade が参考にしたのは、「Vallado, David ‘Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications’, (2007)」だ、と言ってる。論文か何かかしらね? ワタシがここまで書いてきたやつと全く同じなのかどうか細かくはみてないけど、まぁ驚くような差異はないようにみえるわね。